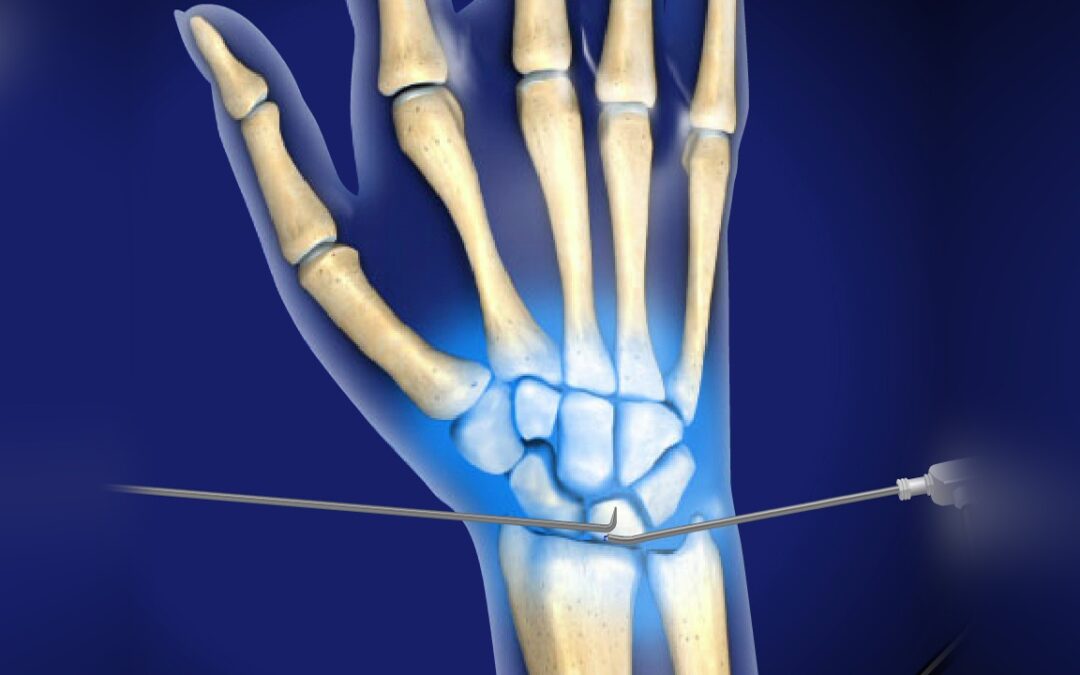
Wrist Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that allows a surgeon to view the inside of a joint. It is often used to diagnose and treat problems in the wrist, such as:
- Tendinitis: This is inflammation of a tendon.
- Tendon tears: This is a tear in a tendon.
- Cartilage damage: This is damage to the smooth, slippery tissue that covers the ends of bones in a joint.
- Fractures: This is a break in a bone.
- Infections: This is a condition where germs invade the body and cause illness.
During wrist arthroscopy, the surgeon makes several small incisions in the wrist. A thin, tube-like instrument called an arthroscope is inserted through one of the incisions. The arthroscope has a camera on the end of it, which allows the surgeon to see inside the wrist on a video monitor.
The surgeon may also insert other instruments through the incisions. These instruments can be used to remove damaged tissue, repair torn tendons, or fix fractures.
Wrist arthroscopy is usually performed as an outpatient procedure. This means that you will be able to go home on the same day as your surgery. You will need to wear a splint or cast for several weeks after surgery. You will also need to do physical therapy to regain range of motion and strength in your wrist.
The recovery time for wrist arthroscopy is usually short. Most people are able to return to their normal activities within a few weeks.
Wrist arthroscopy is a safe and effective procedure for diagnosing and treating problems in the wrist. It may in certain cases be used as an alternative to open surgery, which is a more invasive procedure.