Ganglion Surgery
A ganglion is a fluid-filled sac that can develop in the hand or wrist. Ganglions are usually not painful, but they can be unsightly and can interfere with movement. Ganglions can be treated with non-surgical methods, such as aspiration or splinting, but surgery may be necessary in some cases.
Who is a good candidate for ganglion surgery?
Ganglion surgery is a good option for people who have tried non-surgical treatments for ganglion without success. Non-surgical treatments for ganglion include:
- Aspiration: The surgeon uses a needle to remove the fluid from the ganglion. The ganglion usually recurs following aspiration as the joint fluid recollects.
- Splinting: The surgeon may recommend wearing a splint or brace to immobilize the area around the ganglion. Usually, this is not very successful in trying to get rid of a ganglion.
If you have tried these treatments and your ganglion is still causing problems, you may be a good candidate for ganglion surgery.
What are the risks of ganglion surgery?
The risks of ganglion surgery are:
- Infection
- Nerve damage
- Scarring
- Recurrence of the ganglion
What happens during ganglion surgery?
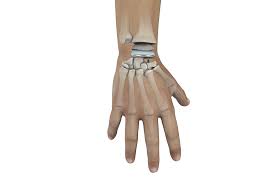
Ganglion surgery is usually performed under local anaesthesia. An incision is made on the skin over the ganglion and the ganglion is excavated and excised including its connection (stalk) with the joint. The incision is then stitched closed, and a bulky dressing put on.
How long does ganglion surgery take?
Ganglion surgery typically takes 30-60 minutes and you can go home on the same day after surgery.
What is the recovery time for ganglion surgery?
The recovery time for ganglion surgery is typically 1-2 weeks. You will need to wear a bandage or dressing over the incision for 1wekk. You will also need to avoid strenuous activity for 1-2 weeks.
What are the results of ganglion surgery?
Ganglion surgery is usually very successful in removing the ganglion and relieving symptoms. However, there is a risk of recurrence of the ganglion.
Here are some additional tips for patients considering ganglion surgery:
- Be realistic about your expectations. Ganglion surgery will remove the ganglion but there is always a risk of it coming back.
- Choose a board-certified hand surgeon with experience in ganglion surgery.
- Ask your surgeon about their aftercare plan.
- Be prepared for a lengthy recovery period.
- Be patient with your results. It can take up to a year for your hand to fully heal.
Here are some frequently asked questions about ganglion surgery:
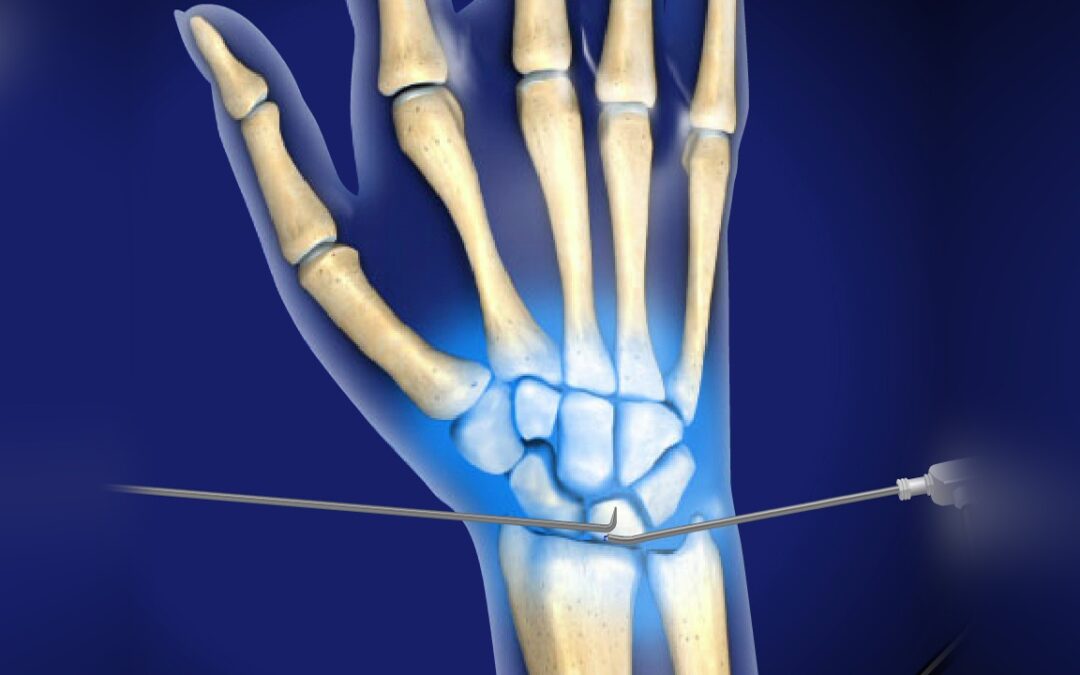
- What is the difference between open surgery and arthroscopic surgery for ganglion? Open surgery is the traditional method of performing ganglion surgery. Arthroscopic surgery is a newer procedure that is performed through smaller incisions. Arthroscopic surgery is generally less invasive than traditional ganglion surgery, but it may not be as effective in removing the ganglion in all cases.
- Can my ganglion be removed arthroscopically? Arthroscopic ganglion removal is usually employed in specific cases where the ganglion is located in a hard to reach place such a deep within the wrist joints.