Wrist Arthritis
Arthritis is a condition that causes inflammation of the joints. It can affect any joint in the body, including the wrist. Wrist arthritis can be caused by a number of things, including:
- Injury: A wrist fracture or dislocation can damage the cartilage in the wrist, leading to arthritis.
- Age: Wrist arthritis is more common in people over the age of 40.
- Occupational overuse: People who use their wrists repetitively, such as factory workers or athletes, are more likely to develop wrist arthritis.
- Genetics: Some people are more likely to develop wrist arthritis than others due to their genes.
What are the symptoms of wrist arthritis?
The symptoms of wrist arthritis can vary from person to person. Some common symptoms include:
- Pain: The most common symptom of wrist arthritis is pain. The pain can be sharp or dull and can be worse with activity.
- Stiffness: The wrist may feel stiff, especially in the morning or after a period of inactivity.
- Swelling: The wrist may swell, especially with activity.
- Weakness: The wrist may feel weak and it may be difficult to grip objects.
- Deformity: In some cases, the wrist may develop a deformity, such as a hump or a lump.
How is wrist arthritis diagnosed?
Your doctor will diagnose wrist arthritis based on your medical history, a physical examination, and imaging tests. Imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRI scans, can help to confirm the diagnosis and see how much damage has been done to the cartilage in the wrist.
How is wrist arthritis treated?
The treatment for wrist arthritis depends on the severity of the condition. Mild cases of wrist arthritis can often be managed with non-surgical treatments, such as:
- Rest: Avoiding activities that put stress on the wrist can help to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Ice: Applying ice to the wrist for 20 minutes at a time, several times a day, can help to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Compression: Wrapping the wrist with an elastic bandage can help to reduce swelling.
- Elevation: Elevating the wrist above the heart can also help to reduce swelling.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help to relieve pain and inflammation. In some cases, your doctor may prescribe stronger medications, such as steroids or cortisone injections.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help to improve range of motion and strength in the wrist.
More severe cases of wrist arthritis may require surgery. There are a number of different surgical procedures that can be used to treat wrist arthritis, including:
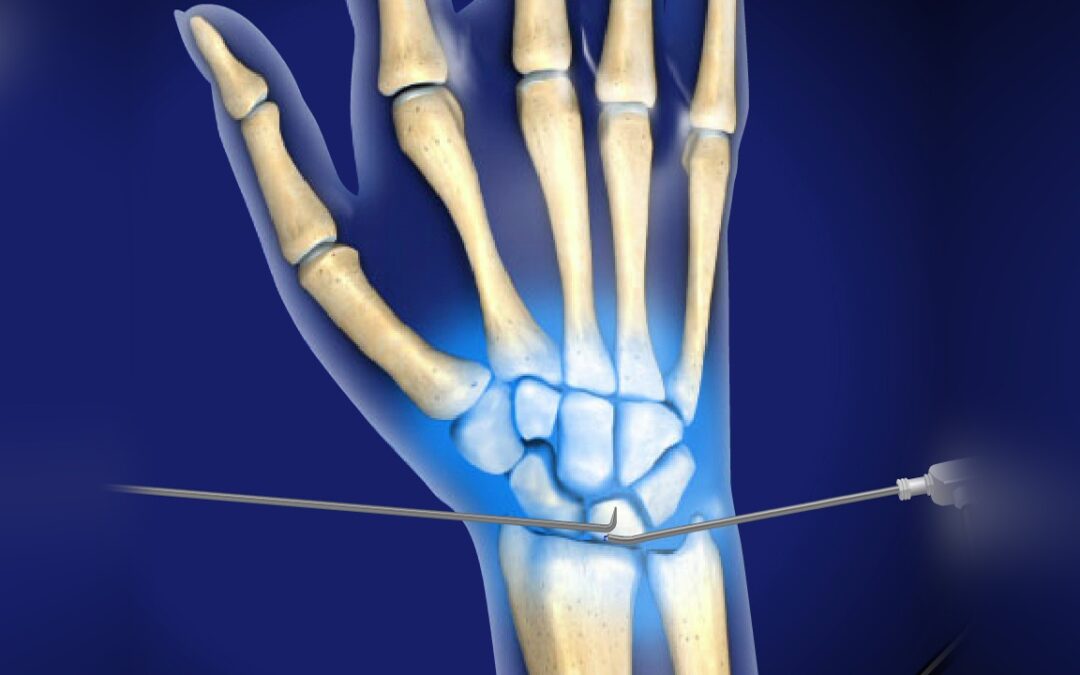
- Arthroscopy: This minimally invasive procedure allows the surgeon to view the inside of the wrist and make repairs without making a large incision.
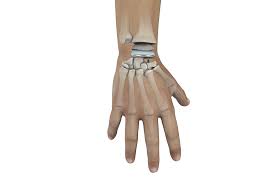
- Wrist fusion: This procedure fuses the bones in the wrist together, which can relieve pain and improve stability.
- Wrist replacement: This procedure replaces the damaged joint with an artificial joint.
What is the prognosis for wrist arthritis?
The prognosis for wrist arthritis varies from person to person. However, most people with wrist arthritis are able to manage their symptoms and continue to live active lives.
If you are experiencing pain or stiffness in your wrist, it is important to see a doctor to get a diagnosis and treatment. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to prevent further damage to the joint and improve your quality of life.